Understanding Poverty in America: A Comprehensive Analysis
Poverty remains a persistent and multifaceted issue in the United States, impacting millions of individuals and families across the country. Despite being one of the world’s wealthiest nations, a significant portion of the population struggles to meet basic needs, highlighting deep-seated economic disparities and social challenges.
Defining Poverty in America
In the United States, poverty is typically defined using income thresholds established by the federal government. As of recent data, the poverty threshold for a family of four was set at approximately $26,500 annually. Individuals and families earning below this threshold are considered to be living in poverty. However, poverty is not merely about income; it encompasses broader aspects of deprivation, including limited access to quality education, healthcare, housing, and economic opportunities.
Key Statistics on Poverty
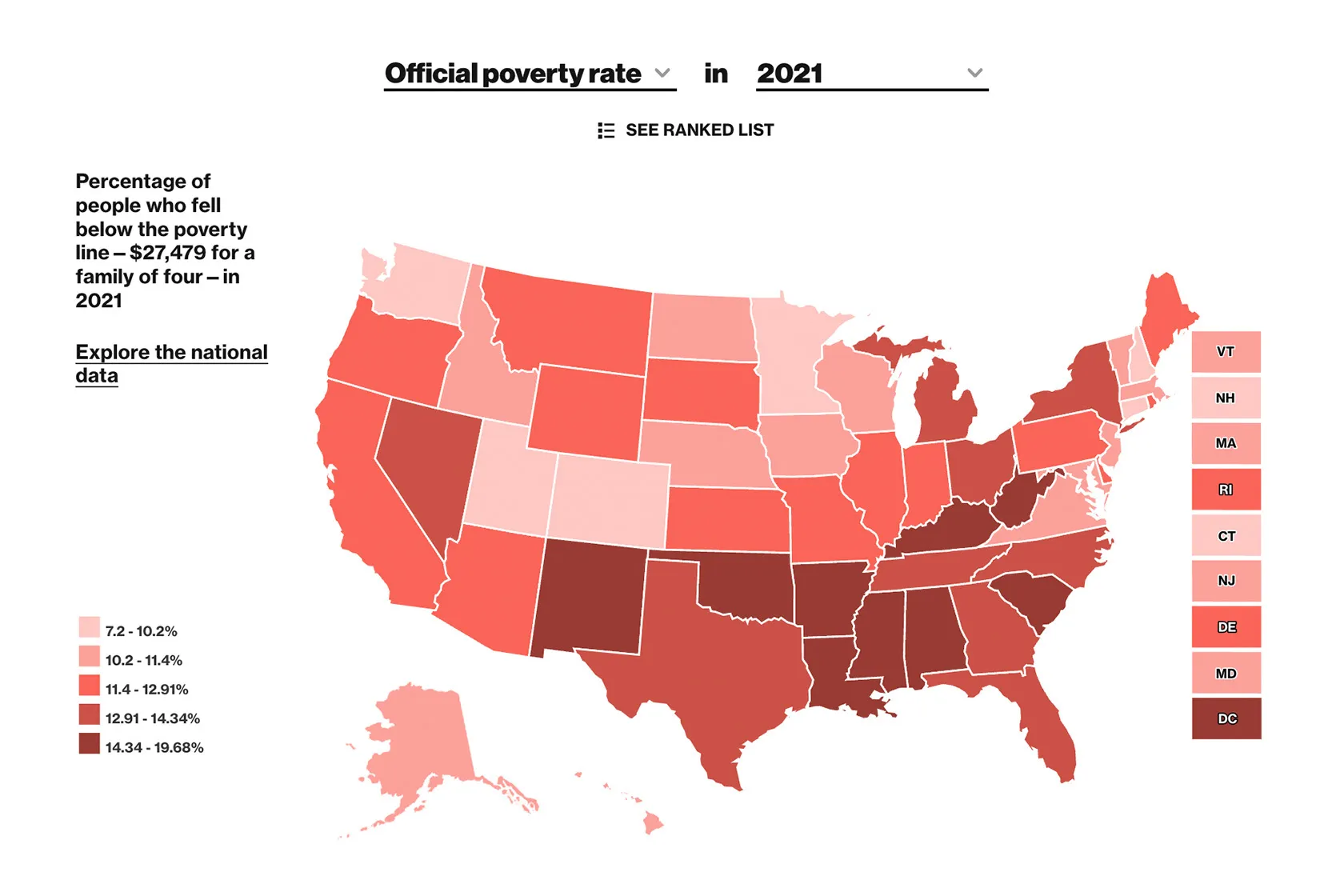
Recent statistics from the U.S. Census Bureau reveal that as of 2023, approximately 11.4% of the U.S. population—equivalent to around 37 million people—lived below the poverty line. Children under the age of 18 are disproportionately affected, with over 14% living in poverty. Poverty rates vary significantly across demographic groups, with Black and Hispanic individuals experiencing higher rates compared to their White counterparts.
Causes of Poverty
The causes of poverty in America are complex and interconnected, influenced by a combination of economic, social, and structural factors. Low wages and income inequality play a crucial role, as many low-income workers struggle to make ends meet despite being employed. Additionally, economic downturns, job losses, and shifts in industries can exacerbate poverty rates, leaving individuals and families vulnerable to financial instability.
Lack of affordable housing is another critical factor contributing to poverty. Rising housing costs in many urban areas often force low-income families into substandard living conditions or homelessness. Furthermore, limited access to quality education and healthcare perpetuates cycles of poverty, as individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds face barriers to obtaining the skills and resources needed for economic mobility.
Impact of Poverty
The impacts of poverty extend far beyond financial hardship, affecting various aspects of individuals’ lives and societal well-being. Health disparities are pronounced among low-income populations, who often lack access to adequate healthcare services, leading to higher rates of chronic illnesses and shorter life expectancies. Children growing up in poverty face educational challenges, including lower academic achievement and higher dropout rates, limiting their future opportunities for success.
Socially, poverty can contribute to social exclusion and marginalization, as individuals and families struggle to participate fully in their communities and access opportunities for social mobility. Economic instability and uncertainty further perpetuate cycles of poverty, creating barriers to upward mobility and reinforcing intergenerational poverty within families.
Addressing Poverty: Policy Recommendations
Addressing poverty in America requires comprehensive and coordinated efforts across multiple fronts, including policy reforms and investments in social programs. Advocates for poverty reduction often propose raising the federal minimum wage to ensure that all workers earn a living wage that meets basic needs. Additionally, expanding access to affordable housing through subsidies and investment in low-income housing programs can alleviate housing insecurity and homelessness.
Improving educational opportunities and job training programs is crucial for equipping individuals with the skills and qualifications needed to secure higher-paying jobs and break the cycle of poverty. Investing in early childhood education and supportive services for families can also have long-term benefits in reducing poverty and promoting economic mobility.
Enhancing social safety nets such as Medicaid, SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program), and unemployment benefits provides critical support to low-income families during times of economic hardship, ensuring access to healthcare, nutrition, and basic necessities.
Poverty remains a significant challenge in America, reflecting broader systemic inequalities and socioeconomic disparities. By addressing the root causes of poverty through targeted policies and investments, society can work towards creating a more equitable and inclusive society where all individuals have the opportunity to thrive.
Efforts to combat poverty must prioritize economic justice, social equity, and community empowerment to ensure that every individual has access to the resources and opportunities needed to achieve economic security and well-being. By fostering a collective commitment to poverty reduction, policymakers, advocates, and communities can create positive change and improve the quality of life for millions of Americans affected by poverty.
